Suncare Essentials > Skin Types: Pigment and Ability to Tan
Ultraviolet radiation from sunlight affects everybody's skin to some extent, but the skin's response varies widely from person to person. Peoples' sensitivity to the sun varies according to the amount of pigment in the skin and the skin's ability to tan.
Ultraviolet radiation causes tanning in two different ways: by immediate tanning and by delayed tanning. Immediate tanning causes the skin to darken in response to UVA. This darkening begins during the period of exposure, but fades within a few hours or days. The amount of tanning increases according to the skin's natural darkness and previous amount of tanning.
Delayed tanning occurs two to three days after exposure to either UVA or UVB. It lasts from several weeks to months, and is maintained by repeated exposure to sunlight. With delayed tanning, the skin increases its production and distribution of dark pigment. The skin also becomes thicker. These changes can follow sunburning or develop gradually over a long period of repeated brief exposures to sunlight.
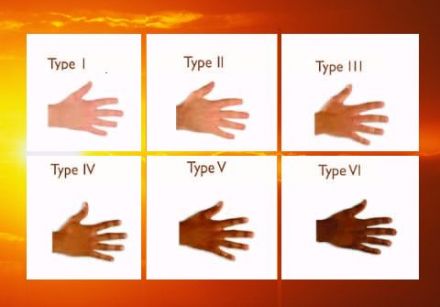
Some people burn easily after the first hour of sun exposure following winter or any period away from the sun. Other people, especially those with dark skin, never burn. This difference in reaction makes it possible to classify skin into one of six different types:
| Skin Type | Hair | Carnation | Freckles | Sun reaction / burns | Tanning / Tans |
| I | Red or Blond | Very fair | +++ | Always | Never |
| II | Blond | Fair | ++ | Often | Lightly |
| III | Blond or light brown | Fair to medium | + to 0 | Sometimes | Progressively |
| IV | Brown | Olive or mate | 0 | Rarely | Rapidly |
| V | Brown to black | Dark | 0 | Rarely | Deeply |
| VI | Black | Very dark | 0 | Never | Deeply |



| Spas | Care & Make-up | Health | For Men | Glossaries | Various | |||||
| Intro | Face (care) Make-up Body Hair Endless Youth Mother & Baby Corner Suncare Essentials And more... New products Spot A HairdresserMake-up Artist Directory | Healthy Diet Watching your figure Relaxation | Intro New products | All about... | Phytotherapy All Natural Fashion Perfume Jewelry & accessories And more... What is your style? |
-

 Spas
Spas
-
 Care & Make-up
Care & Make-up
-

 Health
Health
-
 For Men
For Men
-
 Glossaries
Glossaries
-
 Various
Various